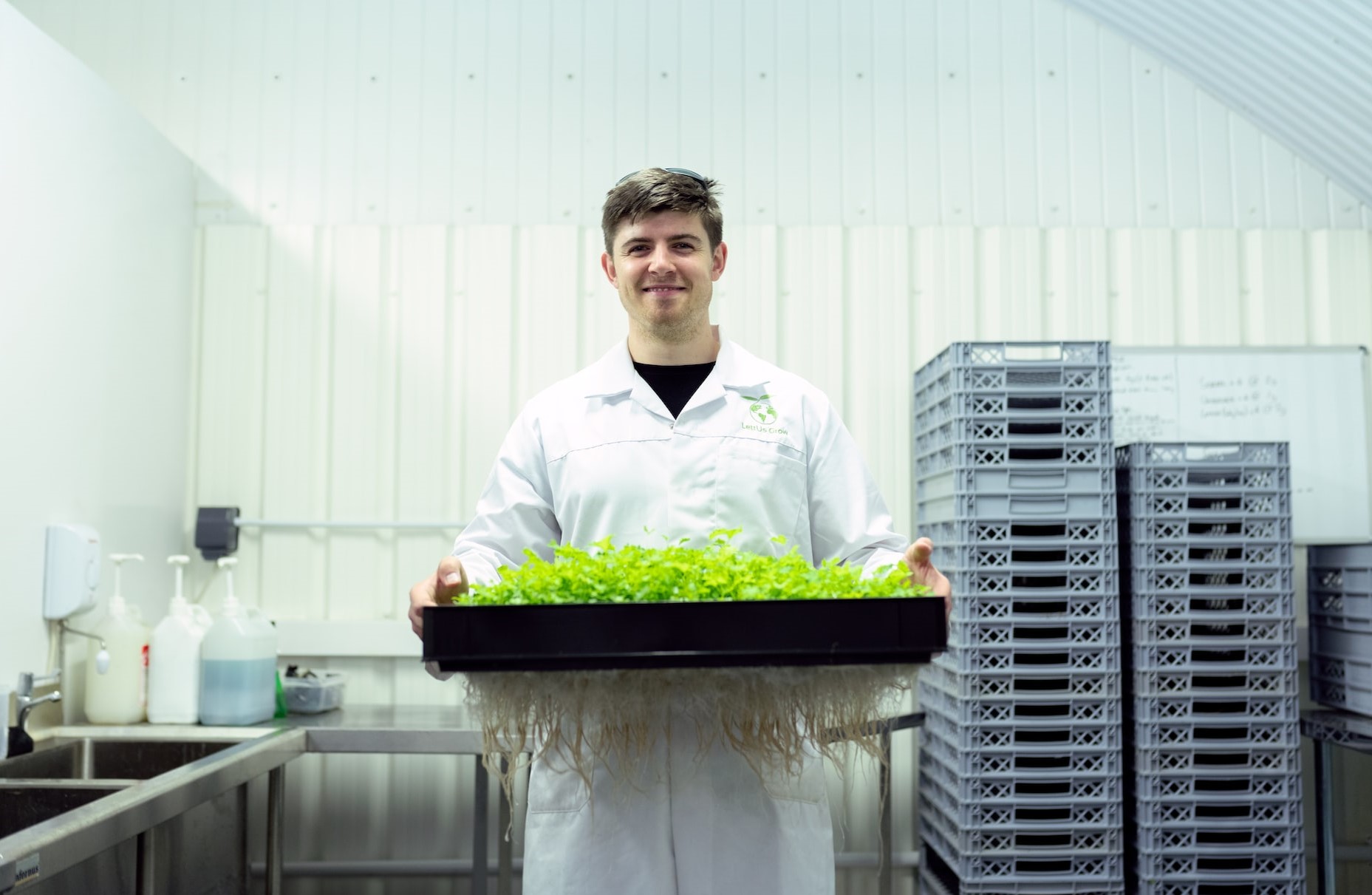
Becoming a food scientist is not as easy as you may think. While it could be said that a food scientist is someone with scientific and math knowledge, one can obtain specific other requirements for this position through education.
It requires considerable hard work and dedication, but it is possible!
How to Become a Food Scientist?
You can start your journey as a food scientist by obtaining your secondary school diploma and a bachelor’s degree. Certifications and credentials are necessary too. Then start looking for internship opportunities and then employment in your area of competence. Finally, continue your education to acquire updated, in-depth knowledge and abilities like pursuing a master’s degree in food science.
These seven easy steps will help you begin your preferred career path as a food scientist. Let’s get started!
1. Start by Obtaining Your Secondary High School Diploma
To become a food scientist, you must have a secondary school diploma or an equivalent education.
Obtaining your secondary school diploma is essential before applying to universities. Food scientists frequently enroll in bachelor’s programs to develop their knowledge and increase employability.
But here’s the kicker, mathematics, social sciences like economics, and science programs are a few beneficial high school electives. The fact is this experience and learning are essential in both the work of a food scientist and the remaining training.
Computer and business courses are also beneficial in preparing for this career!
2. Achieve a Bachelor’s Degree in Food Science
A food scientist must complete a four-year university education after high school to earn a bachelor’s degree in this field. Your primary study areas will be chemistry, biochemistry, microbiology, and technology.
As you go through your program of study, you begin studying specialized courses like food engineering, food chemistry, food processing, and food analysis.
Depending on the university, this degree might cost anywhere from $8,246 to $22,378 annually. Of course, the student’s home state’s public universities offer lower tuition.
As you can see, you will have a fantastic chance to grow your professional network by studying at a university with others who share your interests.
Creating a network in the field as you study could provide you access to extra learning opportunities and mentoring or helpful criticism!
3. Obtain Other Certifications and Credentials
After graduating from college, you can take a standard certification route by enrolling for the Graduate Certificate in Food Science and Technology.
Additionally, the Institute of Food Technologists offers a credential known as a Certified Food Scientist. Non-members must pay $750 for the exam, while members have to pay $550.
Let’s assume you did not take the path of a college degree. Then another certification program for food scientists is the Diploma of Food Science and Technology, which lasts 12 months.
Or consider the American Society for Quality’s Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point (HACCP) as another option.
Generally, you are regarded as a priority and considered for top positions if you are a qualified food scientist.
Food scientists must complete this substantial training and certifications to succeed in this profession. When high-earning positions are available, the cost and duration of this education are deemed worthwhile!
4. Acquire Food Science Internship
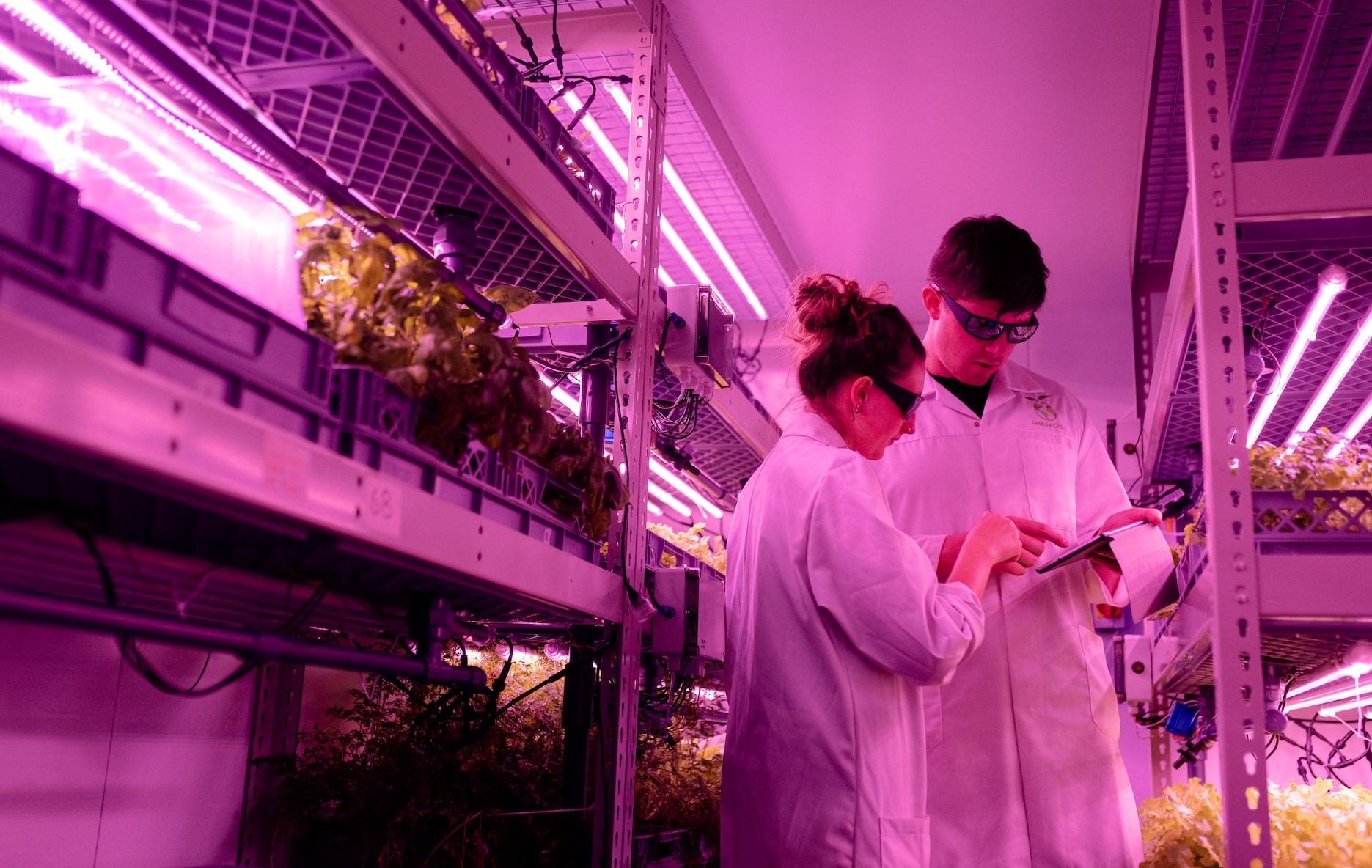

You can gain work experience and connections in the sector through an internship. Organizations that might have ongoing relationships with your school are governmental organizations, food processors, and packaging companies.
Internships in food science frequently concentrate on specific product categories, such as dietary supplements, food safety, or plant proteins.
You might research new ingredients, experiment with unfamiliar ingredients in the kitchen, or assist in offering suggestions for ongoing research projects in one of these programs.
Enrolling in a food science program, fulfilling company-specific requirements, and being experienced with statistical data analysis are the main conditions for obtaining a food science internship.
5. Get Your First Job in Food Science
When applying to jobs as a food scientist, ensure your resume highlights
- skills,
- training,
- certificates,
- licenses, or,
- former employment relevant to the position.
Your ticket to significant job positions, especially senior ones, will be an exceptional portfolio. So spend time and effort developing a solid portfolio in food science.
However, the compensation range for food scientists varies depending on several variables, including
- education level,
- professional experience,
- certifications, and
- other personal skills
According to ZipRecruiter, a food scientist in the United States makes an average of $78,565 a year with $35.64 per hour working.
Employers may ask you to participate in job interviews when you apply for positions so they can find out more about who you are, your qualifications, and your experiences.
In addition to this, you can work in manufacturing, healthcare, engineering, and the culinary arts!
6. Pursuing a Master’s Degree and Ph.D.
A master’s in food science is generally required to apply for most senior or leadership-based positions.
For those who are very interested in academia and research, in addition to a master’s degree, there are also Ph.D. options available, which will give you in-depth knowledge and expertise in the area.
Depending on the university and the field of study, a doctorate can take between three and four years to complete. At the same time, a master’s degree typically lasts between one and two years.
Depending on the university, a master’s degree can cost anywhere between $11,442 to $26,544.
Through Master’s and Ph.D. advanced courses, students continue learning about specializations within the industry.
7. Continuing Education and Networking
As a food scientist, expanding your professional network is an excellent approach to discovering new employment prospects.
For example, meet other professionals, attend alum events, trade exhibits, or social networking websites.
Look for an experienced food scientist who can serve as your mentor and offer you guidance and support. You can discover how they obtained their objectives.
Another great way to learn is through food science editorials and journals like Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety and Nature Sustainability.
By keeping up with the most recent food science research, you may advance in your profession and maintain your understanding of the field!
Conclusion
Keep in mind that there is no single route to becoming a food scientist. Instead, each job lists its requirements and qualifications, so your best bet is to choose one that appeals to you the most and focus on that path.
Ultimately, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics food science is growing at 8% annually with 4100 new job openings yearly. If you are genuinely interested in this field, do your research thoroughly and be sure you are prepared for the food science career path.